Note
Click here to download the full example code
Plotting text¶
It is often useful to add annotations to a map plot. This is handled by
pygmt.Figure.text.
import os
import pygmt
Basic map annotation¶
Text annotations can be added to a map using the text method of the
pygmt.Figure.
Full details of the GMT6 command text can be found `here<https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/latest/text.html>`_. The Python binding to this command is documented `here<https://www.pygmt.org/latest/api/generated/pygmt.Figure.text.html>`_.
Here we create a simple map and add an annotation using the text, x,
and y arguments to specify the annotation text and position in the
projection frame. text accepts ‘str’ types, while x, and y
accepts either ‘int’ or ‘float’ types.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
with pygmt.config(MAP_FRAME_TYPE="plain"):
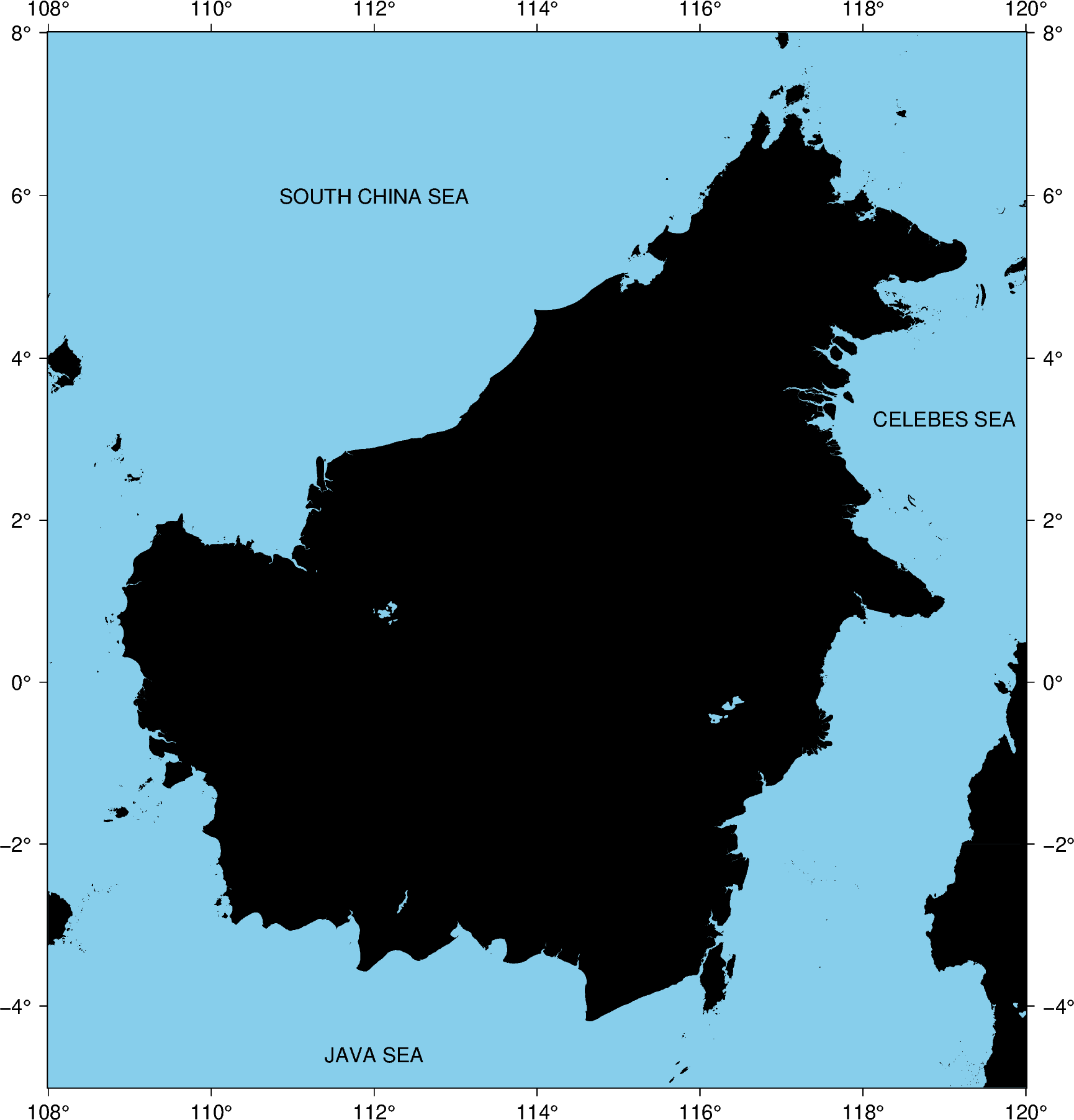
fig.basemap(region=[108, 120, -5, 8], projection="M20c", frame="a")
fig.coast(land="black", water="skyblue")
# Plotting text annotations using single elements
fig.text(text="SOUTH CHINA SEA", x=112, y=6)
# Plotting text annotations using lists of elements
fig.text(text=["CELEBES SEA", "JAVA SEA"], x=[119, 112], y=[3.25, -4.6])
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
Changing font style¶
The size, family/weight, and colour of an annotation can be specified using the font argument.
A list of all recognised fonts can be found `here<https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/latest/cookbook/postscript_fonts.html>`_), including details of how to use non-default fonts.
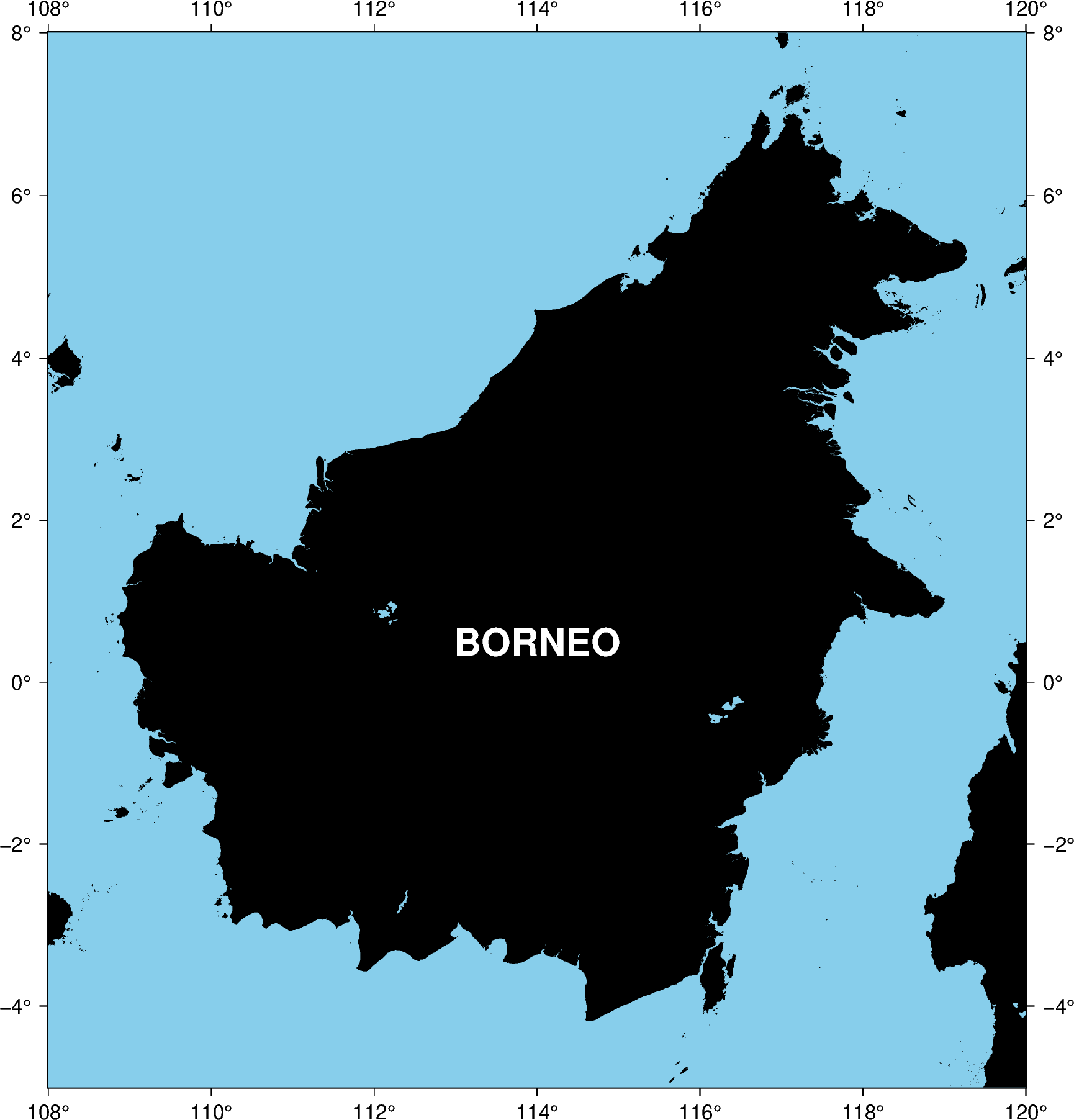
fig = pygmt.Figure()
with pygmt.config(MAP_FRAME_TYPE="plain"):
fig.basemap(region=[108, 120, -5, 8], projection="M20c", frame="a")
fig.coast(land="black", water="skyblue")
# Customising the font style
fig.text(text="BORNEO", x=114.0, y=0.5, font="22p,Helvetica-Bold,white")
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
Plotting from a text file¶
It is also possible to add annotations from a file containing x, y, and text fields. Here we give a complete example.
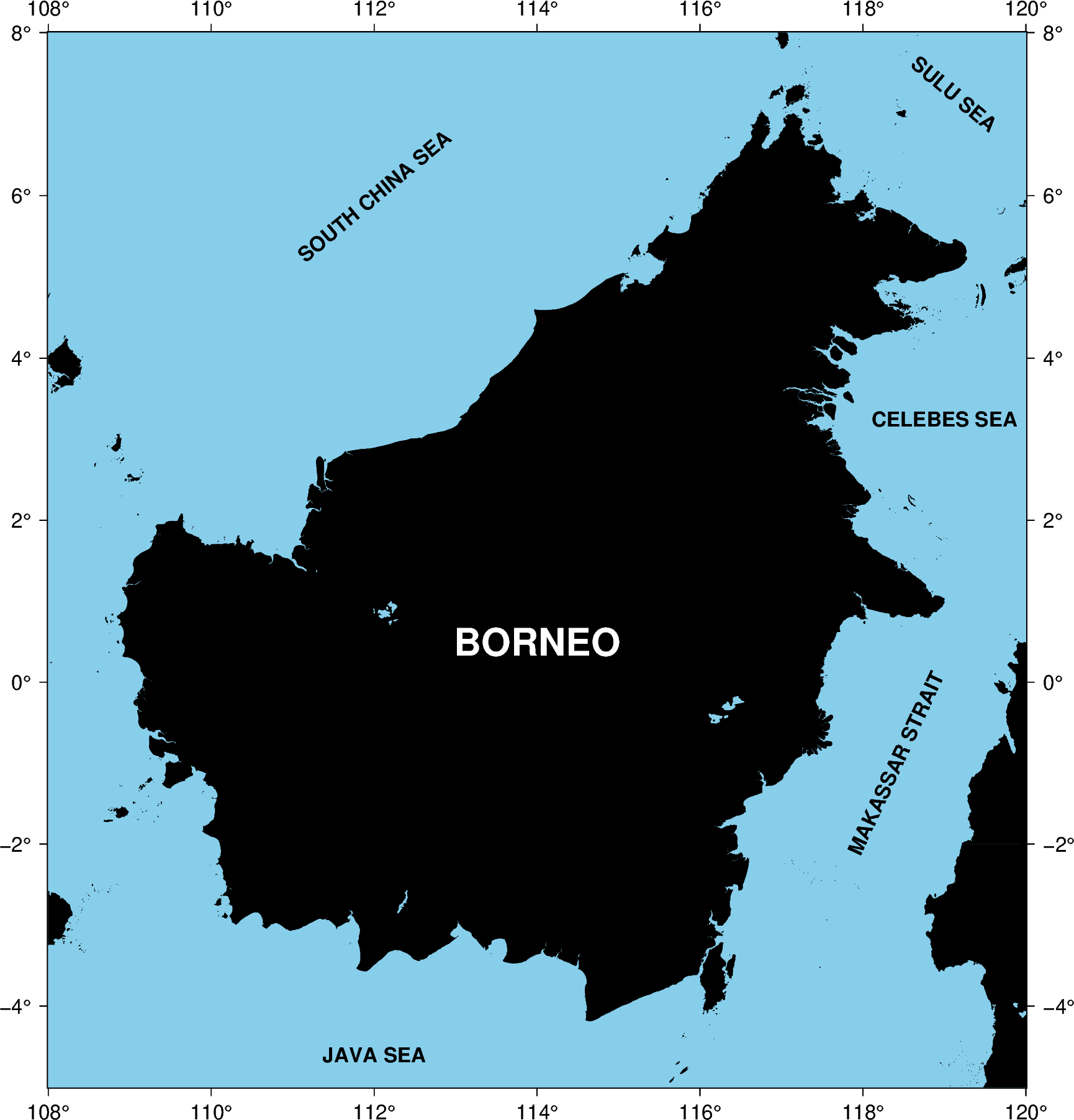
fig = pygmt.Figure()
with pygmt.config(MAP_FRAME_TYPE="plain"):
fig.basemap(region=[108, 120, -5, 8], projection="M20c", frame="a")
fig.coast(land="black", water="skyblue")
# Create space-delimited file
with open("examples.txt", "w") as f:
f.write("114 0.5 0 22p,Helvetica-Bold,white CM BORNEO\n")
f.write("119 3.25 0 12p,Helvetica-Bold,black CM CELEBES SEA\n")
f.write("112 -4.6 0 12p,Helvetica-Bold,black CM JAVA SEA\n")
f.write("112 6 40 12p,Helvetica-Bold,black CM SOUTH CHINA SEA\n")
f.write("119.12 7.25 -40 12p,Helvetica-Bold,black CM SULU SEA\n")
f.write("118.4 -1 65 12p,Helvetica-Bold,black CM MAKASSAR STRAIT\n")
# Plot region names / sea names from a text file
fig.text(textfiles="examples.txt", angle=True, font=True, justify=True)
# Cleanups
os.remove("examples.txt")
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
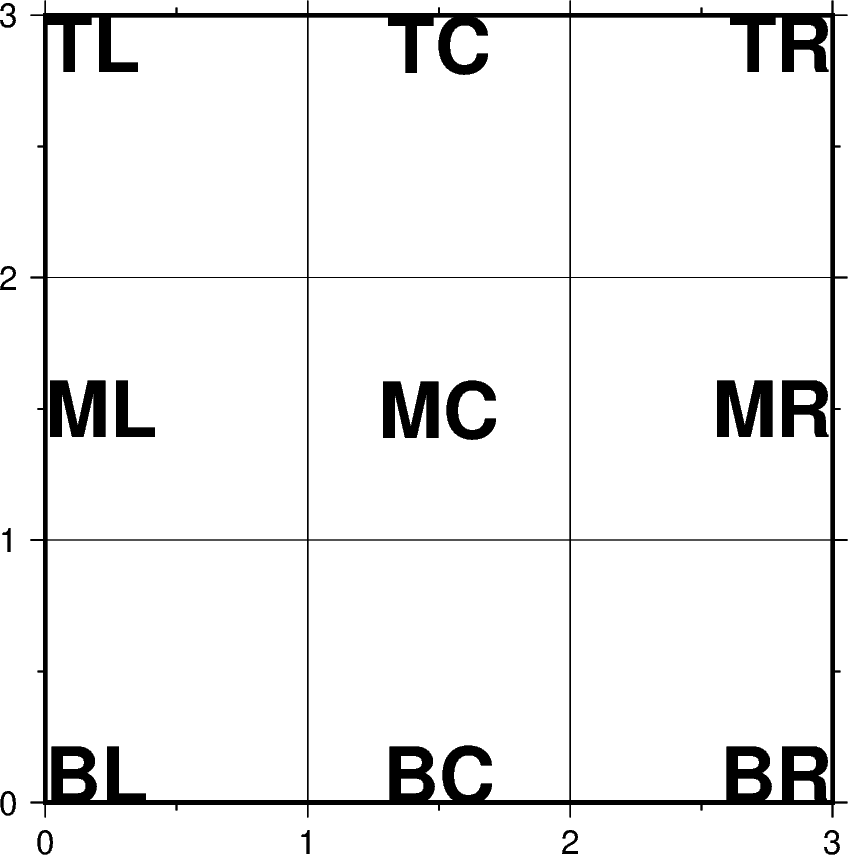
justify argument¶
justify is used to define the anchor point for the bounding box for text
being added to a plot. The following code segment demonstrates the
positioning of the anchor point relative to the text.
The anchor is specified with a two letter (order independent) code, chosen from: * Vertical anchor: T(op), M(iddle), B(ottom) * Horizontal anchor: L(eft), C(entre), R(ight)
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.basemap(region=[0, 3, 0, 3], projection="X10c", frame=["WSne", "af0.5g"])
for position in ("TL", "TC", "TR", "ML", "MC", "MR", "BL", "BC", "BR"):
fig.text(
text=position,
position=position,
font="28p,Helvetica-Bold,black",
justify=position,
)
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
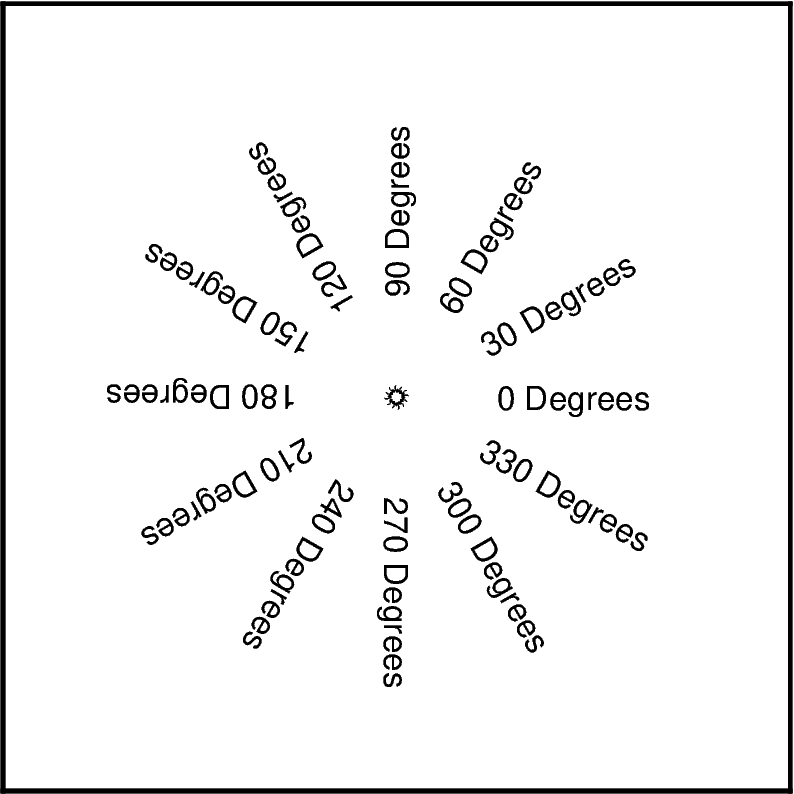
angle argument¶
angle is an optional argument used to specify the clockwise rotation of
the text from the horizontal.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.basemap(region=[0, 4, 0, 4], projection="X10c", frame="WSen")
for i in range(0, 360, 30):
fig.text(text=f"` {i} Degrees", x=2, y=2, justify="LM", angle=i)
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
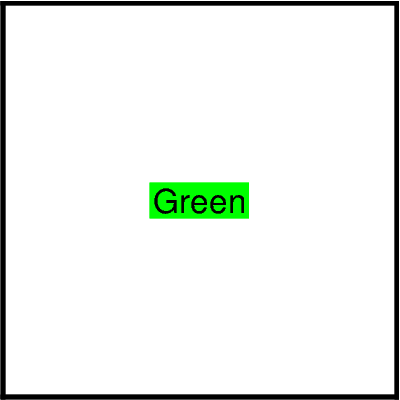
Additional arguments¶
Text can be further configured by passing an argument corresponding to the flag names in GMT, following the same convention as described in the GMT documentation. It is hoped that over time more bindings to these arguments will be written into PyGMT.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.basemap(region=[0, 1, 0, 1], projection="X5c", frame="WSen")
fig.text(text="Green", x=0.5, y=0.5, G="green")
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 4.830 seconds)